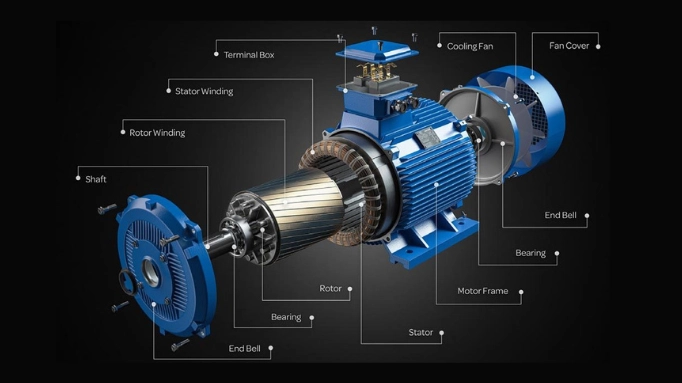
Electric Motors
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor’s magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor’s shaft
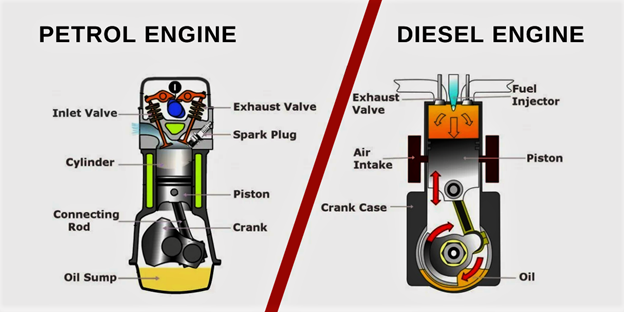
Gas & Diesel Engine
A diesel engine does not use a spark. It’s also called a compression combustion engine, which means it has a higher compression ratio than a gas engine. The air-fuel mixture is squeezed so much that it explodes on its own. Essentially, a gasoline engine is a spark-fired combustion, and a diesel engine uses compression.

PIPE FITTINGS
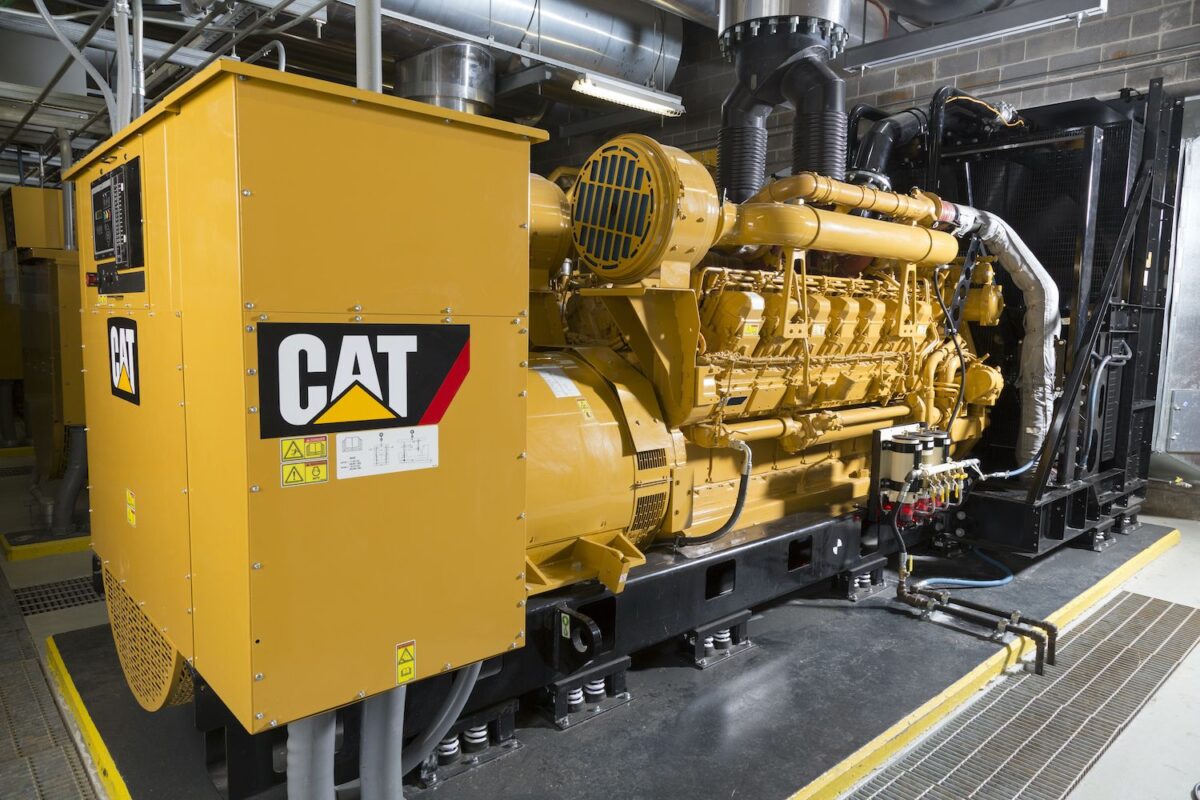
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power (potential and kinetic energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.
In addition to electricity- and motion-based designs, photovoltaic and fuel cell powered generators use solar power and hydrogen-based fuels, respectively, to generate electrical output.
The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators are very similar. Many motors can generate electricity from mechanical energy.
